|
Dr. Pimchai Chaiyen's Laboratory
: Current Research |
Flavin-dependent enzymes : OXYGENASE (1)
1) A two-component enzyme, p-hydroxyphenylacetate hydroxylase from Acinetobacter baumannii.
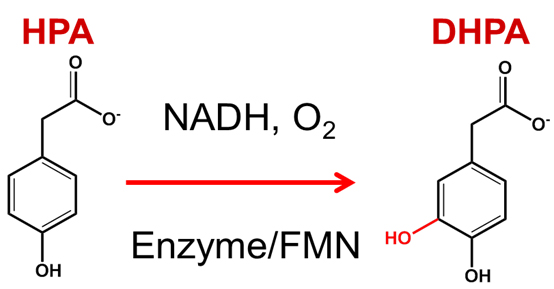
HPAH catalyzes hydroxylation of p-hydroxyphenylacetate (HPA) to form 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate. We isolated and characterized HPAH from Acinetobacter baumannii, and found that the enzyme is a two-component enzyme, consisting of a smaller reductase component (C1) and a larger oxygenase component (C2) (Chaiyen et al., 2001). C1 is isolated with an FMN bound, while C2 is isolated with no cofactor. The function of the reductase is to generate reduced FMN (FMNH-) to be used in the oxygenase reaction. (See pictures).
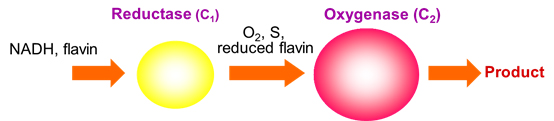
Chaiyen et al., Eur. J. Biochem, 2001
Both components were cloned and expressed in E. coli (Thotsaporn et al., 2004). Our previous investigations have elucidated kinetics and mechanisms of each component (Sucharitakul et al., 2005, 2006) and showed that reduced FMN transfer from C1 to C2 occurs through diffusion without requiring protein-protein interactions (Sucharitakul et al., 2007). A key factor to allow the transfer of reduced FMN via free diffusion to be valid for C1-C2 system is that C2 binds to reduced FMN rapidly and tightly.
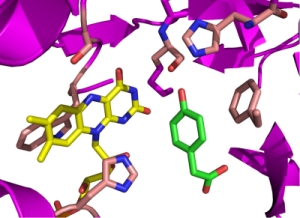
Alfieri et al., PNAS 2007
The X-ray structure of C2 is the first among two-component flavin-dependent monooxygenases to be reported (Alfieri et al., 2007). The three dimensional structures of C2 in three forms, apo C2, C2-FMNH-, and C2-FMNH-HPA, are known. The overall protein folding of C2 is similar to enzymes in the class of acyl CoA dehydrogenase. Multidisciplinary research approaches using molecular dynamics simulations, site-directly mutagenesis and transient kinetics have identified the reaction pathway by which molecular oxygen diffuses through active sites (Baron et al., 2009). Phe266 acts as a gatekeeper for controlling access of oxygen to the active site.
Recent pH-dependent studies have shown that the hydroxylation mechanism of C2 is highly efficient as the enzyme can catalyze a fully coupled hydroxylation throughout a pH range of 6-10 (Ruangchan et al., 2011). Site-directed mutagenesis of Ser171 has shown that the H-bonding interaction between flavin N5 and the hydroxyl group of Ser is important for prolonging life-time of C4a-hydroperoxyFMN, an intermediate that is key for hydroxylation (Thotsaporn et al., 2011). His120 likely exists in protonated form to selectively bind to the phenolat form of the substrate in order to prime the reaction for hydroxylation (Tongsook et al, 2011).
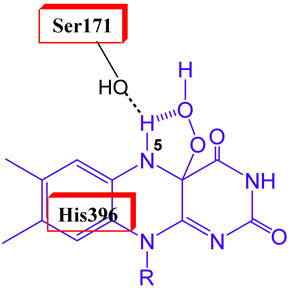
Thotsaporn et al., J. Biol.Chem, 2011
The C1 reductase is unique among two-component flavin-dependent monooxygenases in that its size is about twice that of other flavin reductases. Sequence analysis and homology modeling suggest that the N-terminal domain is a flavin reductase and the C-terminal domain is a regulatory domain (Thotsaporn et al, 2004). Construction of the truncated enzyme has confirmed this hypothesis and shown that the C-terminal domain is an auto-inhibitory domain in which its inhibitory effect can be alleviated when HPA is bound (Phongsak et al., 2012).
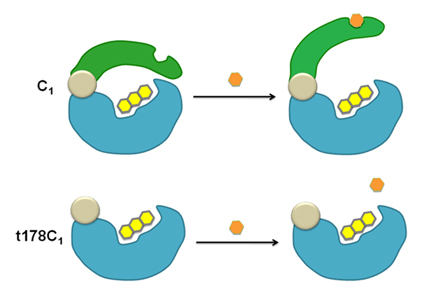
Phongsak et al., J. Biol.Chem., 2012

Current research projects of HPAH
1) Reaction of C2 with substrate analogues and applications of C2 as a biocatalyst
Investigator: Taweesak Dhammaraj
2) Control of oxygen reactivity in C2
Investigator:
Pirom Chenprakhon
Duangthip Trisrivirat
3) Biological significance of C1 and C2
Investigators:
Dr. Kasekarn Kasevayuth
Dr. Kittisak Thotsaporn
4) Novel oxygenases
Investigators:
Panu Pimviriyakul
Kittisak Thotsaporn
Litavadee Chuaboon
[ ...
to continue ... ]

|